|
These medical elastomers can replace thermoset rubber used for tiny plunger tips
or seals that prevent drugs in the tube or barrel of the syringe from flowing
backward as the plunger is depressed. Their good COF also eliminates coating
requirements that might otherwise interact with drug contents of syringes.
These materials also exhibit lower oxygen absorption than nonvulcanizate TPEs
(thermoplastic elastomers), thereby affording greater protection of
pharmaceutical contents when used in seals or gaskets for vials. They also
exhibit greater resilience than other TPEs, perform well in high-temperature end
uses, are more chemical-resistant and can be sterilized in steam, autoclave, or
gamma irradiation processes.
Continuing, polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) resin tailored for medical device
dimensional accuracy is another innovative medical material use example. BASF's
Ultradur B4520 PRO is a recently introduced PBT for injection-molded
applications in medical technology. Its high dimensional stability and optimized
shrinkage behavior meet the stricter reproducible dimensional accuracy
requirements for medical device components. Other property features are as
follows:
-
Sterilized with ionizing gamma radiation or ethylene oxide
-
Can easily be printed on
-
Broad chemical resistance to polar and non-polar solvents
-
Low water/moisture absorption
-
Ideal sliding, due to high friction and wear resistance (depending on the
sliding partner)
-
Excellent heat aging behavior
-
Good moldability with fast cycles
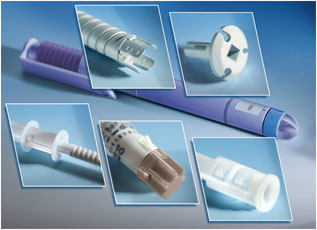
BASF
Functional and mechanical components for insulin pen
Possible medical applications include:
-
Functional and mechanical components with high dimensional precision and
stability for use in drug delivery systems such as insulin pens, inhalers or
metering devices
-
Device components such as manifolds, screws, sleeves, valves, plungers, lancets
or caps
-
Chassis and housings
-
Filter systems
-
Drug containers
-
Pharmaceutical closures
-
Technical disposable applications
Next, polyetherimide (PEI) resisting H2O2 gas plasma sterilization is an
interesting medical plastics material advance. A transparent, high-temperature
thermoplastic, PEl resin blend Ultem HU 1004 from Sabic Innovative Plastics with
improved impact resistance and enhanced hydrostability has been developed for
healthcare applications. Recent tests show that this medical-grade PEI resists
hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) gas plasma sterilization better than polyphenylsulfone
(PPSU) another amorphous high temperature engineering thermoplastic.
There is growing interest in this newer sterilization technique - known
commercially as Sterrad NX, a tradename of Advanced Sterilization Products.
Because this new sterilization technique is a dry, low-heat process, it can be
used to sterilize sensitive electrosurgical devices such as cameras.

Sabic Innovative Plastics/UL IDES
Ultem HU1004 (top row) shows almost no color change from
100 to 300 Sterrad NX
cycles, while PPSU (bottom row)
shows yellowing as early as 100 cycles.
Next
|
