|
India To Create Board To Evaluate Medical Devices
India’s Department of Health Research (DHR) is planning to
establish a Medical Technology Assessment Board (MTAB) to evaluate all types of
new and existing medical technologies.
The MTAB will foster the development of medtech innovations
that will help reduce healthcare costs, improve patient care and streamline the
medical reimbursement procedures. Pharmabiz.com cites sources that claim steps
already have been taken to set up the board and get it operating, though no
specific timetable is mentioned.
The 12th Plan Working Group on Health Research recommended
the establishment of an MTAB. After considering the recommendation, India’s
government decided to create the MTAB to evaluate the need and cost
effectiveness of new and available medical technologies in the country,
pharmabiz’s sources added.
The government plans to consult technology generators,
industry, regulators, economists, user groups and experts knowledgeable about
similar models from the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, Thailand and other
countries before establishing the MTAB. The new agency will be a part of the
overall regulatory / promotional structure being established in the DHR to
accelerate indigenous production of health products/instruments / medical
devices.
As part of the initiative, a Memorandum of Understanding has
been signed between the DHR and the National Institute of Clinical Excellence
(NICE) in the United Kingdom. The two entities are now identifying areas where
they can collaborate on and exchange knowledge about NICE regulatory (first
phase) procedures. An Apex Advisory Committee to set up the board has been
formed and is functional, sources added.
A Parliamentary panel also has called for early action in
setting up the MTAB. “The MTAB is proposed to be assigned with very critical
activities. However, the reply of the Department does not indicate any time
frame within which the MTAB would become functional. A timeline may be fixed for
completing the task,” the panel said.
(Ref:
http://www.mpo-mag.com/contents/view_breaking-news/2014-03-20/india-tocreate-board-to-evaluate-medicaldevices/)
Antimicrobial Plastics Market:
Healthcare / Medical Sector Is By Far The Indisputable Winner
Undoubtedly the Healthcare/Medical sector emerges as first
consumer of antimicrobial, far ahead of packaging according to the recent Click
‘N Vote ‘For which market will the use of antimicrobials grow the most?’ 2014
results are on line with the 2010 click N’ vote results as shown on the Figure 1
below.
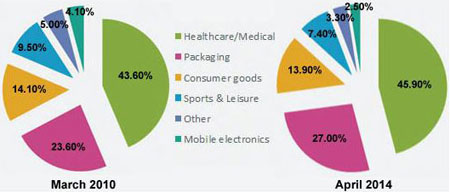
Figure 1: Market to Witness Highest Growth in
Antimicrobials Comparision of March 2010 {220 votes} & April 2014 {122 votes}
Results) Gathered from SpecialChem4Polymers Community Results of the Survey
In fact those similar results hide an intricate and dynamic
evolution due to new trends: more stringent requirements, higher demand,
government regulations, wider range of products used every day, new
environmental trends, new additives, specific solutions. These various
industrial sectors have very different requirements as varied as safety,
lifetime increase, aesthetics, unpleasant odor suppression and sometimes simply
marketing arguments.
Devices are as heterogeneous as medical devices, packaging
products, sports and recreation equipment, Food processing machinery, business
machines, consumer appliances, general household goods, transportation
interiors, construction supplies, outdoor applications and compounds that use
organic fillers.
In addition to technical and economic requirements, the
growth of antimicrobial plastics depends on specific legislative pressures. In
the United States, usage and benefit claims are regulated by the EPA or guided
by the FDA depending on usage. In Europe, The Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR,
Regulation (EU) 528/2012) concerns the placing on the market and use of biocidal
products. All biocidal products require an authorization before they can be
placed on the market, and the active substances contained in that biocidal
product must be previously approved.
All antimicrobial agents have different activities and
varying influences on microorganisms, so every type of antimicrobial solution
must be studied separately depending on the microorganism(s) to be fought.
Antimicrobial solutions include, for example, inorganic
derivatives of Silver, Copper, Zinc and organic products such as BIT (Benzisothiazoline-one),
DCOIT (Dichloro-octyl-4-isothiazolin-one), OIT (Octyl-isothiazolin-one), OBPA (oxybisphenoxarsine),
IPBC (iodopropynyl butylcarbamate), TBT (tributyltin), TBZ (Thiazolyl
benzimidazole), Triclosan, Zinc pyrithione... Of course nanomaterials are also
used and studied.
As for other new and growing technologies, there are many
controversies concerning the antimicrobial spreading in the environment, the
possible harmful effect of certain entities notably for long-term use, the
possible bacterial resistance and/or hormonal disruption, the efficiency of some
products in preventing illness and curtailing infection.
Healthcare / Medical Sector:
Complex epidemiological situation, nosocomial infections,
microbial contamination, and infection risks in hospital and dental equipment
have led to an ever-growing need for prevention of microbial infection in these
various areas.
Antibiotic resistance is a serious and growing phenomenon and
has emerged as one of the pre-eminent public health concerns of the 21st
century. A World Health Organization report states that this serious threat is
no longer a prediction but is happening right now in every region of the world
and can affect anyone, of any age, in any country.
Prevention technologies are vital weapons in the battle
against infection and antimicrobial solutions help enhancing infection
prevention and control. A growing interest in recycling some disposable medical
products continues to create opportunities for antimicrobial solutions.
Antimicrobial solutions are used in hospitals, dental
surgeries, care homes and GP practices for products ranging from beds, cubicle
curtains, nurse call systems, wall and ceiling paints, floors, door handles,
handrails, pull cords, and case note holders.
(Ref:
http://www.specialchem4polymers.com/community-pulse/communityinsight.aspx?id=10677
)
|
